How Web 3.0 Blockchain Would Impact Businesses in 2023?

The term “Web 3.0” has been popular in IT communities. But what precisely is Web 3.0 and why is it causing such a stir in the online space? We shall go into the idea of Web 3.0 and examine its enormous significance in this post. Our primary emphasis will be on the crucial part that blockchain technology plays inside the Web 3.0 framework. So, let’s start this road of digital transformation and evolution.
What Is Web 3.0?
The Internet has gone through astonishing changes since its inception. It started as a static platform called Web 1.0 and evolved into the interactive Web 2.0, which introduced social media, online collaboration, and cloud computing. Now, the time of Web 3.0 promises to revolutionize the internet again with new innovations.
This concept of “semantic web” or “decentralized web,” sometimes known as Web 3.0 is a developing idea for the internet’s future. It is an extension of the current web that operates on a decentralized platform. It’s unlike Web 2.0, which relied on technologies like JavaScript, AJAX, mobile computing, and the cloud. The Web 3.0 platform is built on decentralized technologies.
With Web 3.0, data is more easily searchable and processed efficiently, leading to increased trust and accountability. Users can verify the authenticity and accuracy of information more easily. Users can govern and retain ownership of their data while still maintaining data privacy.
Understanding the Evolution: Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
It’s very important to understand Web 3.0’s development from its forebears. Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, in order to appreciate it completely. In every one of these phases, the way we engage with the internet has changed significantly.
-
Web 1.0: The Static Web
The “Static Web,” sometimes known as Web 1.0, first appeared in the early years of the internet. Web pages at this time were largely static and offered users little opportunity for engagement. It was like an online library, where information was presented one-sidedly.
-
Web 2.0: The Interactive Web
The internet changed after the introduction of Web 2.0. Social media, interactive web applications, and user-generated content were all introduced at this time. Users actively participated in online communities by adding material.
-
Web 3.0: A Paradigm Shift
Web 3.0 takes this evolution a step further by leveraging emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Unlike its predecessors, Web 3.0 is not solely driven by centralized entities but aims to empower individuals and communities through decentralization.
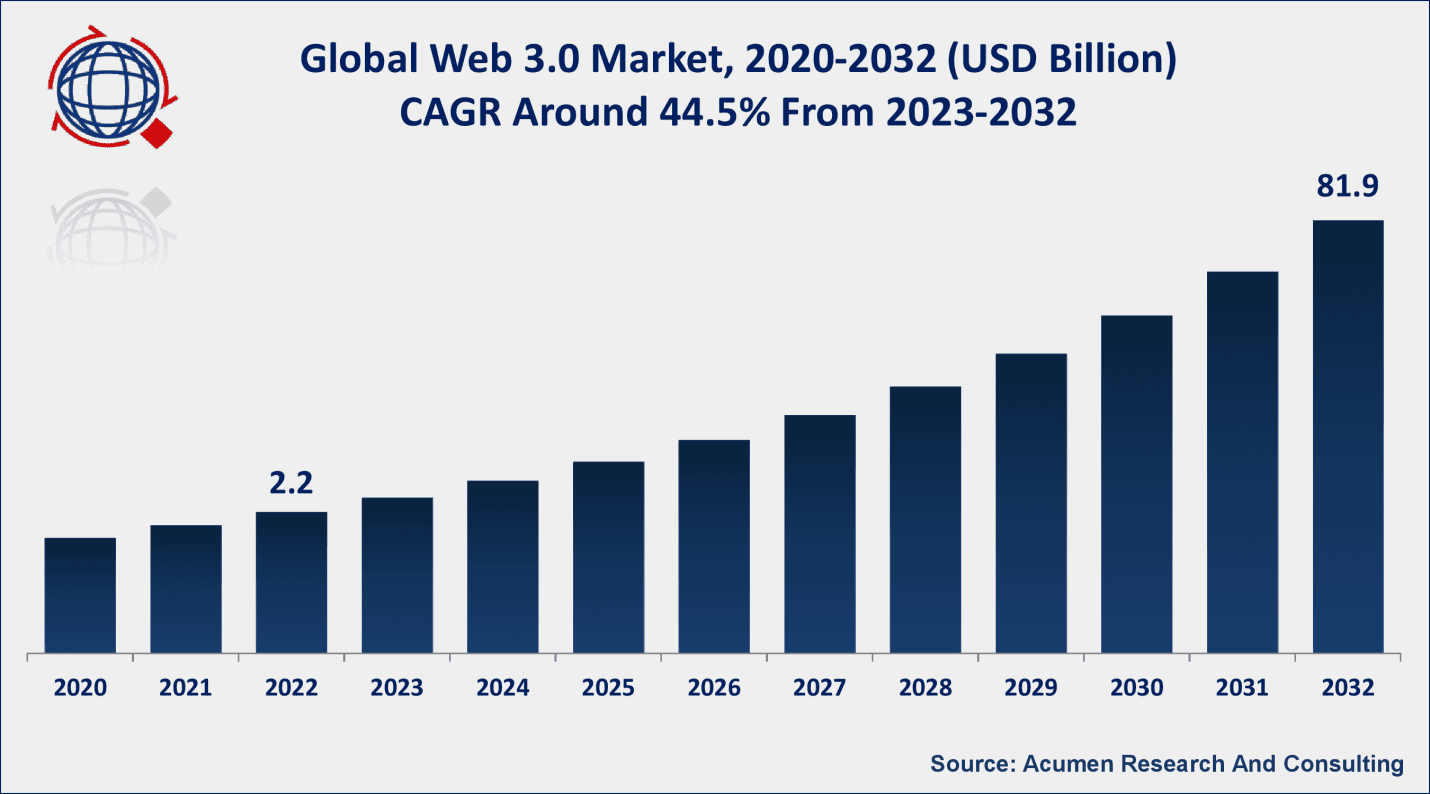
Web 3.0 Market Size
The Global Web 3.0 Market Size reached USD 2.2 Billion in 2022 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 81.9 Billion by end of 2032, growing at an impressive CAGR of 44.5% from 2023 to 2032.
Source: www.acumenresearchandconsulting.com
Highlights of the Web 3.0 Market
- In 2022, the North American region dominated the Web 3.0 market, accounting for over 37% of
the market share. - The Asia-Pacific Web 3.0 market is set to experience substantial growth. With a projected CAGR of around 47% from 2023 to 2032.
- The insurance sector might undergo a change because of blockchain technology. It would be saving $5-10
billion annually by combating fraud and improving claims processing. - In terms of type, the public sub-segment held the majority share of over 54% in 2022.
- The expanding value of the Web 3.0 market is mostly due to the rising need for machine learning
and artificial intelligence.
In a professional tone, it is evident that the Global Web 3.0 Market is experiencing substantial growth and is poised to reach impressive market sizes in the coming years. The Asia-Pacific area exhibits encouraging potential for future growth, while North America has established itself as the industry leader. The value of the Web 3.0 market is also significantly influenced by the increasing need for machine learning and artificial intelligence.
The Future of Web 3.0
How we utilize the internet may be completely transformed by Web 30. Societal acceptance and Technological advancement are the two important factors on which Its future depends.
- Technological Advancements: The continued evolution of Web 3.0 relies heavily on technological breakthroughs. As blockchain, decentralized networks, and smart contracts develop and become more effective, new opportunities will open up . It’s critical to improve scalability, interaction, and user-friendliness. A more reliable Web 3.0 infrastructure will be made possible by innovations like enhanced consensus algorithms and privacy solutions.
- Societal Acceptance: Equally vital is societal acceptance. People are expected to adopt Web 3.0 in greater numbers as they get more familiar with it and its advantages. The advantages and potential downsides of decentralized technologies is essential to be known to the consumers. Public confidence may affect by laws and regulations that define consumer protection.
Key Features and Characteristics of Web 3.0:
Decentralization
Decentralization is the substructure of Web 3.0. Allows users to communicate with one another without the necessity of middlemen. As a result, there is no longer a need for centralized authorities. There is a lesser chance of data breaches, and security and privacy are improved.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
The foundation of Web 3.0 is blockchain technology. Which enables transparent and temper-proof record keeping. On the blockchain, data integrity and transaction legitimacy are guaranteed by a decentralized consensus mechanism. Which is suitable for many applications including supply chain management, decentralized finance and digital identity verification.
Interoperability
The main purpose of Web 3.0 is to increase compatibility amongst various platforms, apps and protocols. Collaboration, creativity and the development of a unified internet environment are all features of Web 3.0. Encouraging seamless data exchange and engagement across various networks.
User Empowerment
Users will have more control over their online identities, data, and actions with the help of Web 3.0. Self-sovereign identification solutions enable people to securely manage their personal data, control who has access to it, and, if they so desire, monetize it.
Enhanced User Experience
To create a personalized and context-aware experience for users Web 3.0 leverages AI, ML and data analytics. With an understanding of user preferences and behavior Web 3.0 applications can deliver tailored content, services and recommendations.
Web 3.0 is quickly emerging as a paradigm shift and the revolutionary power of blockchain technology is at the core of this change. Web 3 is the next stage of the internet, promising a decentralized, user-centric and trustworthy digital environment. There are many sides of Web 3.0 and roll of blockchain technology, fundamentally changing the way we interact with the internet.
Blockchain Technology: The Backbone of Web 3.0
Blockchain technology often referred to as the backbone of Web 3.0 has revolutionized the way we perceive and engage with the internet. Decentralization and trust are the main components of this technology. Including automation, smart contracts, data privacy, and security. Because of these concepts, blockchain has become so critical to the growth of the internet.
Decentralization and Trust
The main conception of blockchain technology is decentralization. This concept might change how the Internet operates now. In traditional centralized systems, a single entity or authority holds control over data and transactions. Censorship, data breaches and the decline of trust are just a few issues caused by this centralized architecture.
Blockchain technology often referred to as the backbone of Web 3.0 has revolutionized the way we perceive and engage with the internet. The main components of blockchain technology are decentralization and trust. They include automation, smart contracts, data privacy and security as well. Because of these concepts, blockchain has become so critical to the growth of the internet.
Same time, by granting people ownership and authority over their digital assets, the decentralized structure of blockchain empowers people. In the world of Web 3.0, users will have the ability to control their data, identity, and digital assets, free from the whims of centralized authorities.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts are Blockchain’s standout features. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms and conditions of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts run on the blockchain, automatically executing when predefined conditions are met. By automating procedures that were formerly laborious and dependent on middlemen.
With its robust potential various industries are expected to change dramatically. As it can help streamline, and automate production processes, reducing the risk of errors and delays. The flow of goods can be monitored with these. This will help suppliers to ensure the authenticity of goods. There are countless options.
The ability to eliminate the need for intermediaries and reduce the potential for human error are the main power of smart contracts. With it not only are processes streamlined but also costs are reduced and efficiency increases. As Web 3.0 continues to evolve, smart contracts will play a central role in automating. A wide range of tasks, from legal agreements to insurance claims.
Data Security and Privacy
A time when data breaches and privacy concerns are rampant, blockchain technology offers a glimmer of hope. The security features of blockchain make it extremely difficult for hackers to compromise data. Because the network is decentralized, there is no single point of failure. Which makes it resistant to attacks. Moreover, the blockchain’s data is encrypted which ensures that only people with permission can access it. Data is at the discretion of the users, who can grant or remove access as they see fit. Blockchain may have a significant impact on the advertising and marketing sector also. Users may have the choice to give their data to advertisers in Web 3.0 in exchange for payment, providing them more control over their online experience and the advertisements they view.
Applications of Blockchain in Web 3.0
The potential applications are vast and far-reaching:
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain-powered DeFi solutions are transforming the financial industry. Without the need for conventional intermediaries, they offer peer-to-peer financing, decentralized exchanges, and digital assets.
-
Web 3.0 Social Networks
Social networks on Web 3.0 will prioritize user privacy and control. Users will own their data and decide how it’s shared. These networks will reward content creators directly, thanks to blockchain-based microtransactions.
-
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR experiences will be revolutionized by Web 3.0. We will see and interact with reality differently as a result of seamless integration with the physical world, improved data overlays, and shared virtual places.
-
Healthcare and Personalized Medicine
In the healthcare sector, Web 3.0 can enable secure, transparent, and interoperable health records. Access to AI-driven diagnoses and individualized treatment strategies will increase.
-
Decentralized Identity Management
The main aim of Web 3.0 is to give people more freedom over their digital identities. Self-sovereign identities, where users have complete control over their personal data, can be created using blockchain technology. Privacy is enhanced and identity theft risk reduced by securely sharing information with trustworthy organizations.
-
Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
The two most well-known cryptocurrencies in the Web 3.0 financial environment are Bitcoin and Ethereum. Providing a decentralized, safe and limitless method of asset transfer. Additionally, non-cryptocurrency assets like fine art and real estate can now be tokenized. Thanks to blockchain technology, them are more easily commoditized and available to a wider audience.
-
Smart Contracts
Self-executing contracts, or “smart contracts,” have predetermined rules and conditions. They abolish the need for middlemen and streamline processes. Applications for smart contracts in Web 3.0 include supply chain management, decentralized finance, and automated legal agreements. Transparency, trust, and effectiveness in transactions are all ensured by them.
-
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Web 3.0 is characterized by the proliferation of DApps built on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polkadot.
From decentralized social networks and gaming to decentralized markets and content-sharing platforms. A vast variety of services are offered by these applications. Users of DApps have greater control over their data and transactions, fostering a more user-centric digital experience.
-
Supply Chain Transparency
Supply chain management becomes more powerful by using the blockchain. It creates an unchangeable record that monitors product location, movement and adherence to regulations. This is especially useful in fields like food and healthcare. Where transparency and traceability are crucial. With blockchain, customers can confirm the genuineness and quality of their purchases, reducing fraud with ensured safety.
-
Data Ownership and Monetization
Users can monetize their data in Web 3.0 by granting access to it through data marketplaces built on blockchain technology. They can choose to give their data to academics or advertisers while still controlling who has access to it and how it is used. This gives people the ability to profit fairly and openly from their data.
-
Content Sharing and Intellectual Property
The compensation of content writers would be revolutionized with blockchain technology. Through blockchain-based platforms, artists, writers, and musicians can receive micropayments directly from consumers, eliminating intermediaries. Besides all these, intellectual property rights can be timestamped and authenticated with blockchain technology by reducing copyright infringement.
-
Voting and Governance
Digital voting systems are safe and impenetrable thanks to blockchain, which guarantees their integrity. In Web 3.0, blockchain-based governance models are emerging, allowing communities and organizations to make decisions through decentralized voting mechanisms. This increases transparency while lowering the possibility of corruption.
-
Energy and Sustainability
When it comes to switching to renewable energy sources blockchain may play a crucial role. It enables transparent monitoring of energy production and consumption. Which facilitates energy trading. In doing so, sustainability is promoted and reliance on centralized energy systems is decreased.
Challenges and Concerns
Like any prospective technology, there are some problems with blockchain that need to be fixed. whether they’re going to succeed and be extensively used. Here are some of the key hurdles that the Web 3.0 ecosystem faces:
Scalability
- Challenge: Scalability remains a persistent challenge for blockchain networks, especially when it comes to handling a large number of transactions per second. Popular blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum have faced bottlenecks due to their limited throughput capacity.
- Solution: Various solutions are being explored to improve scalability. Layer 2 scaling solutions, such as Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Ethereum’s proposed Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, aim to increase transaction throughput significantly. Additionally, alternative blockchains designed with scalability in mind, like Binance Smart Chain and Polkadot, offer increased capacity.
Regulatory Landscape
- Challenge: The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies is evolving rapidly and can be quite complex.
- Solution: The frameworks for compliance and licensing can help the blockchain industry become legal while discouraging illegal activities.
User Adoption
- Challenge: Realizing the full potential of Web 3.0 depends on widespread user adoption, and achieving this can be a gradual process. Users may be hesitant to transition from familiar centralized services to decentralized alternatives.
- Solution: Education and user-friendly interfaces are vital to overcoming this challenge. Projects and DApps in the Web 3.0 ecosystem should focus on providing seamless and intuitive user experiences.
Interoperability
- Challenge: For Web 3.0 to succeed, several blockchain networks must achieve interoperability. The smooth transfer of data and assets may be hampered by the current fragmentation of blockchains.
- Solution: Initiatives like cross-chain bridges and interoperability protocols (e.g., Polkadot and Cosmos) aim to connect different blockchains, enabling them to communicate and share data.
Security and Privacy
- Challenge: Potential dangers including smart contract problems, hacking, and data leaks must be handled.
- Solution: Security risks can be reduced through regular security audits, thorough testing and the use of best practices when creating smart contracts.
Energy Efficiency
- Challenge: The energy consumption associated with some blockchain networks, particularly proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains, has raised environmental concerns.
- Solution: Transitioning to more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake (PoS), is one way to address this issue. PoS blockchains like Ethereum 2.0 aim to reduce energy consumption while maintaining security and decentralization.
Regulatory Landscape
Blockchain technology and the regulatory landscape that surrounds it are dynamic and unpredictable. International organizations, financial institutions and governments all have an impact in this critical context.
All of them aim to establish guidelines and regulations for the exchange of and use of cryptocurrencies as well as the underlying blockchain technology.
Key Aspects of the Evolving Regulatory Landscape Include:
- Classification: How to classify cryptocurrencies is the biggest challenge in the current time. Different jurisdictions categorize them differently – as currencies, securities, commodities, or something else entirely. The taxes system, reporting requirements and legal obligations can all be greatly impacted by this classification.
- AML/KYC Compliance: Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations are being extended to cryptocurrency exchanges and service providers in many countries. This requires them to collect user data, verify identities and report suspicious activities. Which can be at odds with the pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrencies.
- Taxation: Taxation policies for cryptocurrencies vary widely across countries. Some tax them as assets subject to capital gains tax, while others treat them as currencies. The lack of global consensus on this issue creates challenges for international users and businesses.
- Security Regulations: Regulators are also concerned with the security of digital assets and the prevention of fraud. They may require cryptocurrency businesses to adhere to cybersecurity standards and implement measures to protect consumers.
- Exchange Regulations: Cryptocurrency exchanges are a focal point for regulation. Authorities may require licenses, impose trading restrictions, or establish reporting requirements for exchanges. The goal is often to prevent market manipulation and fraud.
- Stablecoins: Stablecoins, which are designed to maintain a stable value, are under increasing scrutiny. Regulators may require them to retain reserves or adhere to certain regulatory criteria because they are worried about their potential impact on financial stability.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Cryptocurrencies are inherently borderless, which complicates regulation. Preventing money laundering and tax evasion is the main aim of regulation of cross-border transactions.
- Consumer Protection: Protecting consumers from fraud, scams, and market volatility is a priority for regulators. This involves making sure that investors are aware of the hazards connected with cryptocurrencies and giving clear information on these risks.
- Innovation vs. Control: There is an ongoing debate between encouraging blockchain and cryptocurrency innovation and maintaining control over the financial system. Regulators face a huge problem in finding the ideal balance.
- International Coordination: Due to the global nature of cryptocurrencies, international coordination among regulators is essential. Common rules for bitcoin regulation are being established by groups like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
User Adoption of Web 3.0
Achieving broad user adoption in the Web 3.0 landscape is our primary goal, albeit a complex and time-intensive endeavor. We work as capable counsel in this burgeoning blockchain industry. Smart contracts and decentralized apps (dApps), demystify complex ideas and highlighting the benefits of improved privacy, security, and data ownership.
Building a user-friendly infrastructure, negotiating the complex regulatory environment, encouraging network effects and creating trust through security measures and open business practices are all among our main priorities. Participation is further improved via user-centric design, scalability solutions, and incentives.
We must be patient as we wait for Web 3.0 technologies to mature, understanding that big changes in technology adoption call for gradual, but ultimately revolutionary growth.
Conclusion
Thus, as Web 3.0 emerges, powered by blockchain technology, we stand on the brink of a new digital era. Our digital interactions are transformed by all the improvements in privacy, security, and data management offered by blockchain.
The potential to spur innovation and provide social benefits is huge. While challenges and uncertainties lie ahead. A future is ahead where the internet is interconnected, secure, transparent, and empowering for everyone.
Let’s welcome Web 3.0 and be part of this transformative wave! Blockchain-powered Web 3.0 promises a user-centered, decentralized internet. It has an obvious capability to change numerous industries. For embracing Web 3.0 addressing issues and promoting widespread acceptance of blockchain technology are necessary.
Web 3.0 will be propelled by blockchain in order to bring forth a new era of decentralization, trust, automation, and data protection. As the internet evolves, businesses will see the impact of blockchain. Which will provide a more accessible, efficient, and secure digital environment. For the future of the web, adopting this technology is a must not a choice. Welcome to the era of Web 3.0, powered by blockchain.
Strivemindz has a variety of Web 3.0 services to offer. We are here to help users navigate the rapidly changing internet world. With our expertise in creating websites and software with an emphasis on semantic web technologies. Which allows machines to analyze data.
Incorporating blockchains, decentralized apps (DApps), smart contracts, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and optimizing Web 3.0 content are all areas in which we have expertise. In this decentralized ecosystem, we promote data interchange, provide strategic consultation, and place security first. Your dependable partner Strivemindz is committed to keeping on the cutting edge of these innovative technologies. Whether you need to tokenize assets or utilize the possibilities of Web 3.0.
Web 3.0 Blockchain Technology FAQs
How does Web 3.0 impact data privacy?
By enabling selective sharing and preventing unauthorized use of it, Web 3.0 gives people more control over their data.
What industries stand to benefit the most from Web 3.0 and blockchain technology?
Financial, supply chain, real estate and healthcare sectors stand to gain a lot from Web 3.0 and blockchain technology advancements.