XaaS in Cloud Computing: How it’s shaping the Cloud Industry in 2024

Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering a wide range of services over the Internet. One of the key developments in cloud computing is the concept of “XaaS” or “Anything as a Service.” XaaS refers to the delivery of various services over the Internet, including infrastructure, platform, software, network, desktop, and unified communications.
According to the latest research, the global Everything as a Service (Xaas) market size was valued at USD 273163.0 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 26.13% during the forecast period, reaching USD 1099916.05 million by 2028.
This article delves into the intricate world of XaaS, exploring its evolution, key components, benefits, challenges, and profound impact on the cloud industry. As organizations increasingly embrace cloud-based services to enhance agility, scalability, and innovation, understanding the nuances of XaaS models becomes essential in navigating the dynamic landscape of modern IT solutions.
XaaS in Cloud Computing: How it’s Shaping the Cloud Industry
Introduction to XaaS in Cloud Computing
Have you ever heard of “Everything as a Service” (XaaS)? If you’re navigating the world of cloud computing, this term is bound to pop up sooner or later. XaaS represents a significant shift in how businesses access and utilize technology.
In essence, XaaS is a broad term encompassing all the IT resources delivered on-demand over the Internet. Imagine a vast buffet of IT services, from software applications to storage and security, all accessible with just an internet connection.
Understanding XaaS: What Does It Stand For?
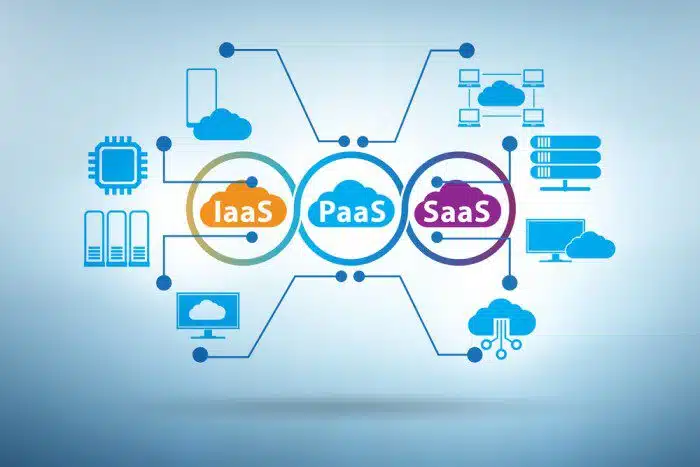
XaaS stands for “Anything as a Service,” and it encompasses a variety of cloud-based services that are delivered over the Internet. These services include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), Network as a Service (NaaS), Desktop as a Service (DaaS), and Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS). Each of these services offers unique benefits and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses.
Overview of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and store data and applications over the Internet instead of on their computers or servers. This technology provides various services, including storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics, all delivered over the internet (“the cloud”). Cloud computing offers several advantages, such as flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. There are different types of cloud computing models, including public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud, each offering different levels of security and control.
Explanation of different types of XaaS Models
XaaS, or “Everything as a Service,” encompasses a vast array of IT resources delivered on-demand over the internet. But with such a broad term comes a variety of service models, each catering to specific needs. Let’s delve into the most common XaaS models to understand their unique offerings:
Software as a Service (SaaS): This is the most widely adopted XaaS model. SaaS applications are readily available over the internet, eliminating the need for local installations or software licenses. Popular examples include CRM software, email services, and project management tools. Benefits include ease of use, automatic updates, and subscription-based pricing.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a cloud-based platform for developers to build, test, deploy, and manage applications. Think of it as a complete development environment readily available online. PaaS solutions offer increased development agility and reduced infrastructure management burdens. Popular examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Microsoft Azure App Service.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This model provides users with access to fundamental computing resources like virtual servers, storage, and networking. Businesses essentially rent these resources from a cloud provider, offering high scalability and control over the underlying infrastructure. Popular examples include Amazon EC2 and Google Compute Engine.
NaaS (Network as a Service): NaaS provides network services over the Internet, including virtualized networking infrastructure, bandwidth management, and security services. It allows businesses to access and manage network resources on demand.
DaaS (Desktop as a Service): DaaS delivers virtual desktops over the internet, allowing users to access their desktop environment from any device. It offers flexibility and scalability, making it an ideal solution for businesses with remote or mobile workers.
UCaaS (Unified Communications as a Service): UCaaS delivers communication and collaboration tools over the internet, including voice, video, messaging, and conferencing services. It helps businesses streamline communication and improve productivity.
Benefits of using XaaS in Cloud Computing
The concept of XaaS, or Everything as a Service, has revolutionized cloud computing. By offering on-demand access to a vast array of IT resources, XaaS empowers businesses to unlock a multitude of benefits. Here’s a closer look at the key advantages of leveraging XaaS in the cloud:
- Enhanced Cost Efficiency: XaaS eliminates the need for hefty upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure. Businesses transition to a pay-as-you-go model, significantly reducing capital expenditures. Additionally, XaaS minimizes the burden of internal IT management, leading to further cost savings.
- Unmatched Scalability and Agility: One of the biggest strengths of XaaS is its inherent scalability. Businesses can easily scale their IT resources up or down based on real-time needs. This agility allows them to adapt quickly to changing market demands and seize new opportunities without significant infrastructure investments.
- Increased Accessibility and Democratization: XaaS makes cloud computing accessible to businesses of all sizes. Even startups with limited resources can access sophisticated IT capabilities, levelling the playing field and fostering innovation. This democratization of technology empowers businesses to compete more effectively.
- Faster Innovation and Development: By eliminating the need to manage and maintain IT infrastructure, XaaS frees up internal IT teams. This allows them to focus on core business applications, develop innovative solutions, and accelerate digital transformation initiatives.
- Improved Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: XaaS solutions like Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) provide businesses with readily available backup infrastructure. This ensures business continuity in the event of disasters or outages, minimizing downtime and potential revenue losses.
- Simplified IT Management: XaaS centralizes IT resource management, simplifying administration tasks. Cloud providers handle maintenance, updates, and security patches, freeing up internal IT resources for more strategic tasks.
- Enhanced Security: Many XaaS providers offer robust security features and compliance certifications. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses that lack the expertise or resources to manage their own security infrastructure effectively.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance: XaaS ensures that businesses always have access to the latest software versions and security patches. Automatic updates eliminate the need for manual installations and minimize the risk of security vulnerabilities.
- Global Accessibility: XaaS allows businesses to access IT resources from anywhere with an internet connection. This facilitates remote workforces, improves collaboration, and empowers businesses to operate in a globalized environment.
Challenges and limitations of adopting XaaS in the Cloud
While XaaS offers a plethora of benefits for businesses in the cloud computing realm, it’s not without its challenges and limitations. Here’s a closer look at some of the potential hurdles to consider when adopting XaaS:
- Vendor Lock-In: Migrating from one XaaS provider to another can be complex and costly. Businesses may become reliant on a specific vendor’s platform, making it difficult to switch providers in the future if needs change or pricing becomes less favourable.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Handing over critical data to a cloud provider raises concerns about security and privacy. Businesses need to be diligent in selecting XaaS providers with robust security measures and clear data ownership policies to ensure their data is protected.
- Performance and Reliability Dependence: XaaS relies heavily on internet connectivity. Businesses with unreliable internet connections may experience performance issues and downtime, impacting business operations. Additionally, they are dependent on the XaaS provider’s infrastructure and security for uptime and performance.
- Limited Customization: While XaaS offers a wide range of services, some solutions may lack the level of customization businesses require for specific needs. Businesses may need to adapt their workflows to fit the XaaS model, potentially hindering flexibility.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating XaaS solutions with existing on-premises infrastructure can be complex, requiring additional time and resources. Businesses need to carefully consider integration compatibility before adopting XaaS solutions.
- Hidden Costs: While XaaS eliminates upfront costs, some hidden costs can creep up over time. These can include data egress fees, API usage charges, and additional storage charges. Careful planning and monitoring of XaaS usage is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Lack of Internal Expertise: Utilizing XaaS effectively may require specialized skills and knowledge. Businesses that lack internal IT expertise might need to invest in training or consider managed service providers to support XaaS adoption.
- Compliance Considerations: Businesses operating in highly regulated industries need to ensure their chosen XaaS solutions comply with relevant data privacy and security regulations. This can add complexity to the decision-making process.
Case Studies showcasing successful implementation of XaaS
The concept of XaaS (Everything as a Service) is revolutionizing how businesses leverage technology. Here are a few compelling case studies showcasing successful XaaS implementations across various industries:
Dropbox and the Rise of SaaS:
- Company: Dropbox, a leading cloud storage provider
- Challenge: Businesses and individuals struggle with managing and sharing large files efficiently.
- Solution: Dropbox pioneered the concept of Software as a Service (SaaS) for file storage and sharing. Users can access their files from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering remote collaboration and simplifying file management.
- Impact: Dropbox’s success highlights the power of SaaS in providing user-friendly and scalable solutions that address everyday business needs.
Netflix and the Power of PaaS:
- Company: Netflix, the global streaming giant
- Challenge: To meet the demands of a rapidly growing user base and deliver a seamless streaming experience globally, Netflix needed a highly scalable and adaptable infrastructure.
- Solution: Netflix adopted a Platform as a Service (PaaS) model built on cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS). This allowed them to develop, deploy, and manage their streaming platform with agility and scalability.
- Impact: Netflix’s success story demonstrates the power of PaaS in enabling businesses to build and deploy complex applications efficiently while handling massive workloads.
Airbnb and the Magic of IaaS:
- Company: Airbnb, the hospitality marketplace leader
- Challenge: Airbnb needed a robust infrastructure to handle a dynamic marketplace with millions of listings and bookings worldwide.
- Solution: Airbnb utilizes Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) from cloud providers like Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This provides them with the virtual servers, storage, and networking resources needed to scale their platform seamlessly.
- Impact: Airbnb’s case exemplifies how IaaS empowers businesses to access essential computing resources on-demand, enabling them to adapt to fluctuating demand and maintain a global presence.
Zoom and the XaaS Advantage in Communication:
- Company: Zoom, a popular video conferencing platform
- Challenge: Businesses needed a user-friendly and reliable solution for remote communication and collaboration.
- Solution: Zoom leverages a comprehensive XaaS model, offering video conferencing as a service (CaaS) with features like screen sharing, recording, and integrations with other business applications.
- Impact: Zoom’s success showcases the power of XaaS in delivering specialized services like communication and collaboration tools readily available over the internet, fostering a more connected and productive work environment.
Future trends and developments in the XaaS industry
The XaaS landscape is a dynamic one, constantly evolving to meet the ever-changing needs of businesses. Here’s a glimpse into some of the exciting trends and developments we can expect to see in the future of XaaS:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: XaaS providers are increasingly integrating AI/ML technologies capabilities into their services. This integration enhances automation, improves data analysis, and enables more personalized and intelligent services.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is gaining traction in the XaaS industry, enabling services to be delivered closer to the end user. This reduces latency, improves performance, and enhances user experiences, particularly for real-time applications.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is being explored for its potential to enhance the security and transparency of XaaS services. It can be used to secure transactions, verify identities, and track data access and usage.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), is becoming more prevalent in the XaaS industry. This model allows businesses to run applications without managing servers, reducing operational complexity and costs.
- IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) is being increasingly integrated into XaaS offerings, enabling businesses to collect and analyze data from connected devices. This integration enhances decision-making, improves efficiency, and enables new service offerings.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Adoption: Businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, leveraging XaaS services from multiple providers. This approach offers greater flexibility, resilience, and optimization of costs and performance.
Also Read: How Cloud Computing contributes to the growth of the Industrial IoT
Conclusion on the impact of XaaS on Cloud Computing
In conclusion, XaaS (Anything as a Service) has had a profound impact on cloud computing, transforming the way businesses access and utilize IT services. XaaS offers a wide range of benefits, including cost efficiency, scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes. However, adopting XaaS also comes with challenges, such as security concerns, compliance issues, and integration complexities, which businesses must address.
Looking ahead, the future of XaaS in cloud computing looks promising, with trends such as AI and machine learning integration, edge computing, and blockchain technology shaping the industry. As XaaS continues to evolve, businesses can expect more innovative and customized solutions that enhance their operations and drive growth.
Overall, XaaS has revolutionized the cloud computing industry, providing businesses with new opportunities to optimize their IT infrastructure, improve efficiency, and stay competitive in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
What are the benefits of XaaS for businesses and users?
XaaS, or Everything as a Service, offers several advantages. It reduces costs, enhances modern applications and business processes, and shifts IT infrastructure to more valuable projects.
What considerations should companies keep in mind before adopting XaaS?
There are various challenges to consider, including proprietary lock-in, data backup and recovery, internet reliability, and operational issues.
Can you provide some examples of successful XaaS implementations?
Certainly! Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk, Apache Stratos, Google App Engine, and Salesforce’s Heroku and Salesforce Platform are all successful examples of XaaS in action.
What emerging technologies are shaping the future of XaaS?
Emerging technologies such as edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain are driving the future of XaaS.
Is XaaS cost-effective in the long term?
XaaS’s pay-as-you-go models often lead to cost savings. However, to ensure long-term cost-effectiveness, businesses must monitor and optimize resource usage closely. Regular evaluations and adjustments to resource allocation help maintain ongoing financial efficiency.