What Is Web 4.0: An Overview of the Latest Evolution of the Internet

What is Web 4.0? As the internet continues to evolve, many people have asked this question. Compared to previous versions of the internet, Web 4.0 represents a major change. What is Web 4.0 and how does it work? We will explain in this blog post. In addition, we will cover the pros and cons of this new technology, as well as answer some frequently asked questions about it.
What Is Web 4.0: It’s Time To Talk About It
A collaborative and interactive approach to web development characterizes Web 4.0, the fourth generation of the World Wide Web. Users can easily share information and ideas with web four point zero applications because they are designed to be user-friendly. Websites such as social networking, blogs, wikis, and video-sharing sites are among Web 4.0’s most popular applications. The concept of web four point zero represents a shift toward an approach that is more collaborative and user-centric rather than traditional web development.
Web 4.0 also called the “Intelligent Web” or “Symbiotic Web,” represents the next step in Internet technology. It combines cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), virtual and augmented reality, and blockchain. Using data-driven insights to enhance our digital experiences, Web Four Point Zero creates a seamless interaction between humans and machines.
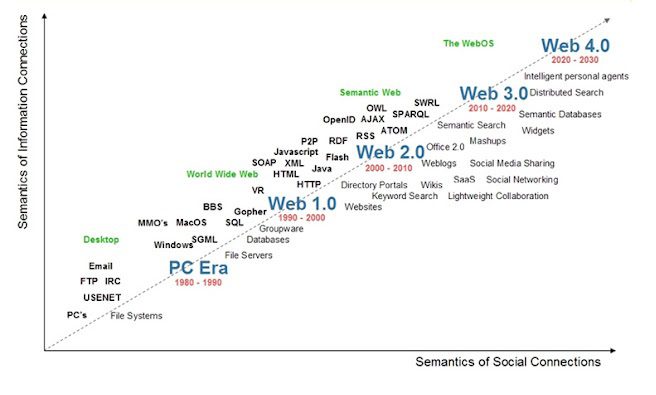
Evolution of Web from 1.0 to 4.0
Certainly, let’s explore the history and characteristics of Web 1.0, Web 2.0, Web 3.0, and introduce the concept of Web 4.0:
Web 1.0 (The Static Web):
- Era: The late 1990s to early 2000s.
- Characteristics: Web 1.0 definition, also known as the “Static Web,” was the initial phase of the World Wide Web. Websites during this era were static, primarily offering text and images with limited user interactions. They served as online brochures, providing information but not much interactivity.
- Technology: HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) was the primary technology used. Search engines like Yahoo and AltaVista were essential for navigating the web.
- Examples: Early websites in this era included online newspapers, corporate homepages, and basic e-commerce sites.
Web 2.0 (The Social Web)
- Era: The mid-2000s and onwards.
- Characteristics: Web 2.0 definition, known as the “Social Web,” introduced significant interactivity and user-generated content. Websites evolved into platforms for social interaction, collaboration, and content sharing. Users could create, share, and modify content, leading to the rise of social media, blogs, wikis, and online communities.
- Technology: Technologies like AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) allowed dynamic content updates without full page reloads, enhancing the user experience. Web 2.0 was characterized by user-generated content and the development of platforms like Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Wikipedia.
- Examples: Social media platforms (e.g., Facebook, Twitter), video-sharing sites (e.g., YouTube), and collaborative platforms (e.g., Wikipedia) represent the Web 2.0 era.
Web 3.0 (The Semantic Web)
- Era: Web 3.0 is an evolving concept without a specific timeframe but gained attention in the early 2000s and continues to develop.
- Characteristics: This definition of Web 3.0, also called the “Semantic Web,” emphasizes the importance of enhancing the web’s capability to comprehend and interpret data. It aims to create a more intelligent and context-aware web, where data is structured and linked for machine comprehension. This enables advanced features like improved search results, better personalization, and automation.
- Technology: Technologies like Linked Data, RDF (Resource Description Framework), and ontologies make data more structured and machine-readable. Web 3.0 leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning for data processing.
- Examples: While still in development, Web 3.0 encompasses concepts like the Internet of Things (IoT), where devices and objects connect to the web, as well as decentralized technologies like blockchain for secure data sharing and smart contracts.
Read also: How Web 3.0 Blockchain Would Impact Businesses in 2023?
Web 4.0 (The Intelligent Web)
- Era: Web 4.0 is a concept under development, not yet widely implemented as of my last knowledge update in January 2022.
- Characteristics: Web 4.0 definition, often referred to as the “Intelligent Web,” represents the latest phase in the internet’s evolution. It incorporates advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, big data, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to create a more interconnected, intelligent, and data-driven digital environment. This enables personalized experiences, efficient automation, and enhanced decision-making.
- Technology: Web 4.0 leverages AI, machine learning, and big data analytics to enable systems to understand and respond to user behavior, making interactions more personalized and efficient.
- Examples: As of the last update, the full realization of Web 4.0 was still in development. It encompasses innovations in AI, IoT, and interconnected systems to revolutionize various aspects of online life.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Web 4.0
Advantages of Web 4.0:
- Enhanced Intelligence and Personalization: Web four point zero leverages advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to deliver highly customized and tailored content and services to individual users.
- Augmented Interactivity: Web four point zero empowers more immersive and interactive experiences, such as virtual and augmented reality, enabling users to engage with information and services in novel and innovative ways.
- Seamlessly Blending Physical and Virtual Realms: Web four point zero acts as a bridge between the physical and virtual worlds through technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), facilitating the connection and integration of real-world objects and environments with digital platforms.
- Greater Decentralization and Democratization: Web four point zero fosters greater decentralization and democratization of information and services, reducing reliance on centralized platforms in favor of peer-to-peer networks and decentralized protocols.
- Improved Security and Privacy: Web four point zero employs advanced cryptographic technologies and decentralized architectures to provide enhanced security and privacy safeguards for users’ data and communications.
Disadvantages of Web 4.0:
- Escalated Technology Dependence: Web four point zero may intensify our reliance on technology and digital platforms, as users become accustomed to highly personalized services designed to fulfill their every requirement.
- Amplified Surveillance and Control Potential: Web four point zero may amplify the opportunities for surveillance and control, as remarkably intelligent and personalized services gather and analyze extensive user data, potentially leading to manipulation or influence of user behavior.
- Increased Complexity and Technical Sophistication: Web 4.0 might entail greater complexity and technical sophistication compared to earlier web iterations, necessitating highly skilled developers and engineers for its design and maintenance.
- Potential for Aggravated Inequality: Web four point zero could exacerbate existing inequalities, as highly personalized services primarily cater to the needs and preferences of the most affluent and influential users, leaving others at a disadvantage.
- Enhanced Vulnerability to Cyber Attacks: Web four point zero could exhibit greater susceptibility to cyber attacks, given its highly interconnected and intelligent systems, which provide more potential targets for malicious actors.
Key Features of Web 4.0
Web 4.0, also known as the “Intelligent Web,” is an evolving concept that represents the latest phase in the internet’s evolution. It incorporates advanced technologies and features to create a more interconnected, intelligent, and data-driven digital environment. Some key features of Web 4.0 include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): At the core of web four point zero is AI, which enables the internet to understand, learn, and adapt. AI systems can analyze user behavior, providing highly personalized and efficient online interactions.
- Big Data Utilization: Web 4.0 harnesses the power of big data. Enormous volumes of data generated by users and devices are collected and analyzed to provide insights, improve services, and support data-driven decision-making.
- Cloud Computing Integration: Cloud computing is the backbone of web four point zero. It offers scalable and flexible resources for data storage and processing. This scalability is crucial to meet the increasing demands of a highly connected world.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT plays a central role in web four point zero It connects devices, sensors, and everyday objects to the internet, creating a network that can share data and perform tasks autonomously. This interconnectedness is transforming various aspects of life, from smart homes to industrial automation.
- Personalization: Web Four Point Zero strives to provide highly personalized online experiences. AI algorithms analyze user preferences and behaviors to offer tailored content, product recommendations, and services.
- Efficiency and Automation: With AI and IoT, Web four point zero offers increased efficiency and automation. This means processes are streamlined, and tasks can be automated, enhancing productivity and convenience.
- Enhanced Security: The interconnectedness of devices and systems in web four point zero raises concerns about security. As a result, there’s a strong emphasis on enhancing digital security and protecting sensitive information from cyber threats.
- Improved Decision-Making: Web four point zero provides better decision support by offering data-driven insights and predictions. Businesses and individuals can make informed choices based on the analysis of vast amounts of data.
- Real-Time Interactivity: Web four point zero enables real-time interactions and dynamic content updates, enhancing the user experience and making online interactions more engaging.
- Data-Driven Innovation: Businesses and industries can leverage data to drive innovation and create new products and services. The ability to analyze user data and market trends enables businesses to stay competitive and adapt to changing demands.
- Cross-Platform Integration: Web four point zero encourages the integration of various platforms and devices, allowing users to seamlessly transition from one device to another while maintaining a consistent and personalized experience.
- Sustainability: Web 4.0 also emphasizes sustainability and resource efficiency. Cloud computing and data optimization, aim to reduce the environmental impact of online activities.
Web Four Point Zero combines these features to create a more intelligent and interconnected digital world, where the internet not only serves as an information source but also as a dynamic, adaptive, and personalized environment that enhances our daily lives and decision-making processes.
Applications of Web 4.0
Web 4.0, with its emphasis on advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT), has a wide range of applications that can transform various aspects of our lives and industries. Some key applications of Web 4.0 include:
- Smart Cities: Web four point zero can play a significant role in the development of smart cities. IoT devices can monitor traffic flow, manage energy consumption, and optimize public services. This leads to reduced congestion, energy efficiency, and improved urban living.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, Web Four Point Zero facilitates remote patient monitoring, AI-assisted diagnostics, and predictive analytics. Patients can receive personalized care, and healthcare providers can make data-driven decisions for better outcomes.
- Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: Web 4.0 is closely tied to Industry 4.0. IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics improve manufacturing processes, enhance quality control, and enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
- Supply Chain Management: Web four point zero enhances supply chain visibility, enabling real-time tracking of goods, inventory management, and demand forecasting. This results in more efficient logistics and reduced costs.
- Retail and E-Commerce: E-commerce platforms leverage the web four point zero to offer personalized product recommendations, optimize pricing, and enhance the overall shopping experience. AI chatbots and virtual shopping assistants also provide customer support.
- Energy Management: Smart grids powered by web four point zero technologies can balance energy supply and demand, incorporate renewable energy sources, and reduce energy wastage.
- Agriculture: Precision agriculture uses IoT sensors and AI to monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather, optimizing crop yields and resource usage.
- Education: Web 4.0 enhances education with personalized learning experiences. AI-driven platforms can adapt curriculum and assessment to individual student needs, making education more effective and engaging.
- Transportation and Autonomous Vehicles: Web 4.0 plays a crucial role in autonomous vehicles and smart transportation systems. AI and IoT technologies enable vehicles to communicate with each other and with traffic infrastructure, enhancing safety and traffic flow.
- Financial Services: In the financial sector, Web 4.0 supports fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and personalized financial advice. Blockchain technology, often associated with Web 4.0, can provide secure and transparent financial transactions.
- Content Recommendation: Web 4.0 enhances content recommendation systems by analyzing user behavior and preferences. This personalization applies to video streaming, news, social media, and e-commerce.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT sensors can monitor environmental conditions, track air and water quality, and help in disaster management and early warning systems.
- Smart Homes: Web 4.0 enables smart home systems to control lighting, heating, security, and appliances, improving energy efficiency and enhancing home automation.
- Public Safety: In law enforcement and emergency services, Web 4.0 supports predictive policing, crisis management, and surveillance, enhancing public safety and response times.
- Entertainment and Gaming: AI and big data analysis enhance the gaming experience, creating more realistic simulations and personalized gameplay.
Web 4.0’s applications are vast and diverse, and they continue to evolve as technology advances. Its impact is felt in everyday life, from the way we live and work to how industries operate and provide services. These applications have the potential to make our world more efficient, connected, and responsive to our needs.
Web 4.0: Why Do We Need It?
As technology evolves day by day, we live in a constantly changing world. Keeping up with the latest trends is essential in order to stay ahead of the curve as new advancements are made every day. The latest trend is web four point zero. But what does that actually mean? Why do we need it?
web four point zero refers to the fourth generation of the World Wide Web. A seamless integration between the physical and virtual worlds is characterized by increased user interaction and collaboration. Users can use social networking, blogs, wikis, folksonomies, mashups, and user-generated content in web four point zero.
One of the main reasons we need Web 4.0 is because it helps us connect better. To build relationships and communities in a digitized world, it is essential to be able to connect with others online.
A more personalized experience is also possible with Web 4.0. Through increased user interaction and collaboration, we can create experiences tailored to our needs. It could be anything from discovering new music to exploring different cultures.
Final thoughts
As a result, Web 4.0 is at the forefront of technological advancement, ushering in a new era of connectivity, intelligence, and innovation. Incorporating artificial intelligence, machine learning, IoT, virtual and augmented reality, and blockchain technology, Web Four Point Zero offers unprecedented opportunities to improve our lives in multiple ways.
Much of what we are saying may indeed seem hyped up and wishful thinking. This is not about selling fantasies, but rather about thinking creatively and imaginatively about the possible outcomes of our technologies in the near future. It will take a few years for companies to jump on web four point zero (it’s still a long way off). Think about connections, integration, symbiosis.
We can harness Web 4.0’s potential to drive positive change, shape industries, and create a future in which the boundaries of possibility are endless.